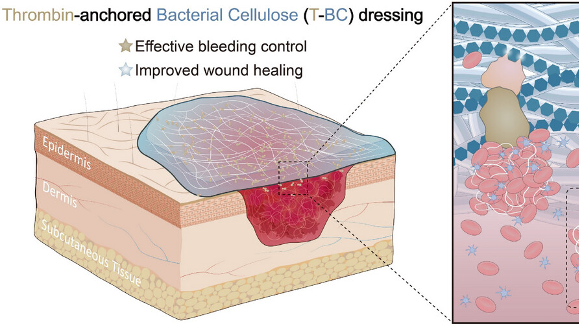
In a game-changing move for burn care, scientists in the Chinese mainland have engineered a bioactive dressing that stops severe wound bleeding in under 60 seconds. The innovation comes from the Chinese mainland's Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in collaboration with Ruijin Hospital.
The team harnessed bacterial cellulose (BC) – a super-breathable, body-friendly material – and anchored the natural blood-clotting enzyme thrombin onto it. By adding a specially designed cellulose-binding domain, thrombin stays locked onto the BC scaffold, turning it into a powerful bleeding blocker.
When applied to burn wounds, the Thrombin-Anchored BC (T-BC) dressing creates an instant seal. Lab tests published in Advanced Materials show it halts bleeding in less than a minute, integrates seamlessly with human skin, and even activates self-repair pathways at the injury site.
This leap from petri dish to potential clinic use could transform emergency care worldwide. For young global citizens, entrepreneurs in medtech, and digital nomads seeking evidence-based health solutions, T-BC offers a peek at how biotech can rewrite critical care narratives.
As materials science meets real-world impact, this bacterial cellulose breakthrough highlights the power of interdisciplinary research and the promise of faster, safer treatment for burn victims everywhere.
Reference(s):
Researchers develop bacterial cellulose-based dressing for burn wounds
cgtn.com